Gold slides as market mood improves due to Trump easing tensions on China
- Gold drops more than $100 from its daily high to $3,288 amid risk-on sentiment.
- Trump says he has “no intention” of firing Fed Chair Powell, calming markets.
- WSJ reports US mulling China tariff cuts; Bessent says no unilateral move yet.
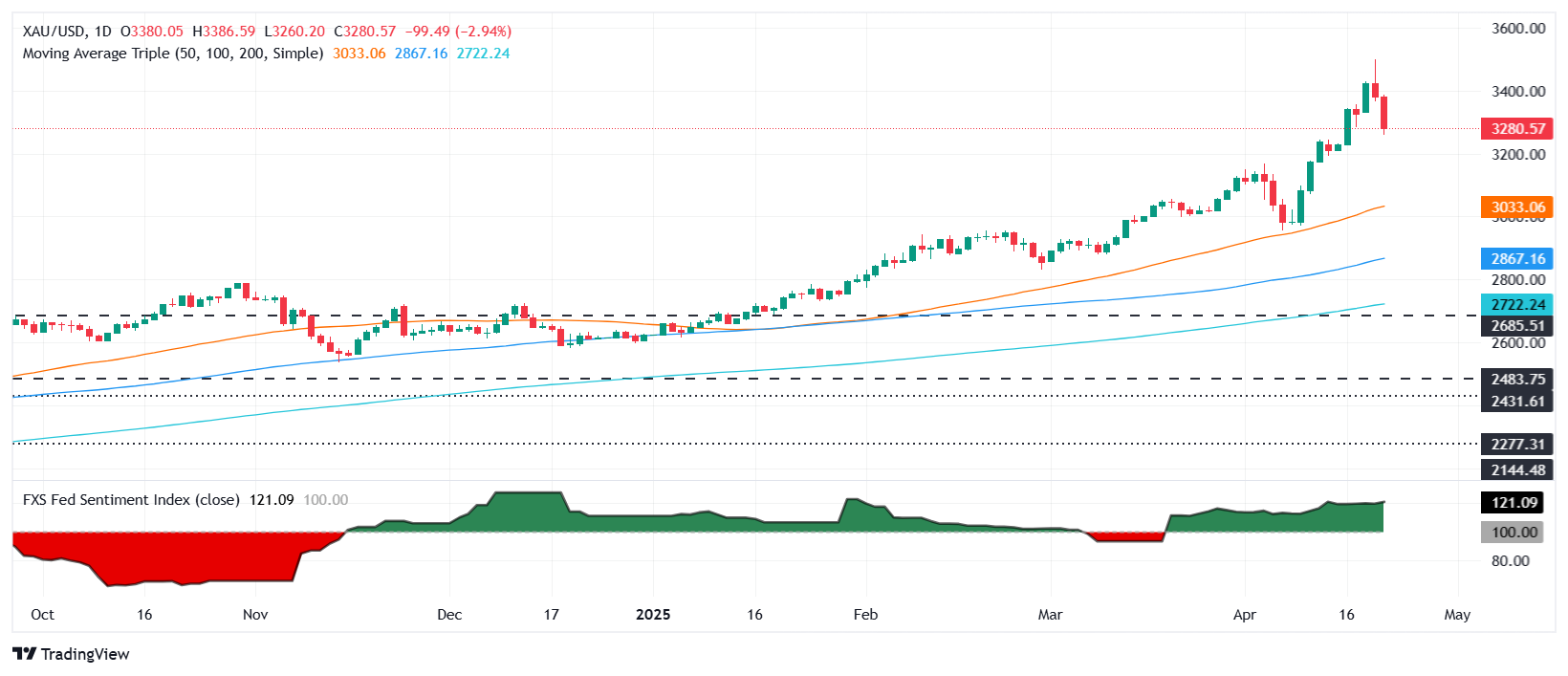
Gold prices plunged more than 2.50% on Wednesday as risk appetite improved due to a possible de-escalation of US-China tensions and US President Donald Trump's statement that he doesn’t plan to fire Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell. At the time of writing, XAU/USD trades at $3,288 after hitting a daily high of $3,386.
The narrative in the financial markets hasn’t changed. Tariffs continued to drive price action, and news that the US might slash duties on China sent US equities higher and Bullion prices tumbling.
An article in The Wall Street Journal suggested this, though US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent poured cold water on traders’ mood. He said Trump has not offered to lower tariffs on Chinese products unilaterally, hinting that China must do its part.
On Tuesday, Trump said he had no intention of firing Powell and added, “The press runs away with things. No, I have no intention of firing him. I would like to see him be a little more active in his idea to lower interest rates.”
Amid these comments, Bullion edged lower as the Greenback recovered some ground. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the American currency value against a basket of six others, is up 0.09% at 99.72.
Regarding the chances of the Federal Reserve reducing interest rates at the upcoming meeting, traders see a 94% chance of keeping them unchanged, according to Prime Market Terminal. Nevertheless, traders expect the Fed funds rate to end at 3.45%, equal to 92 basis points of easing (bps).
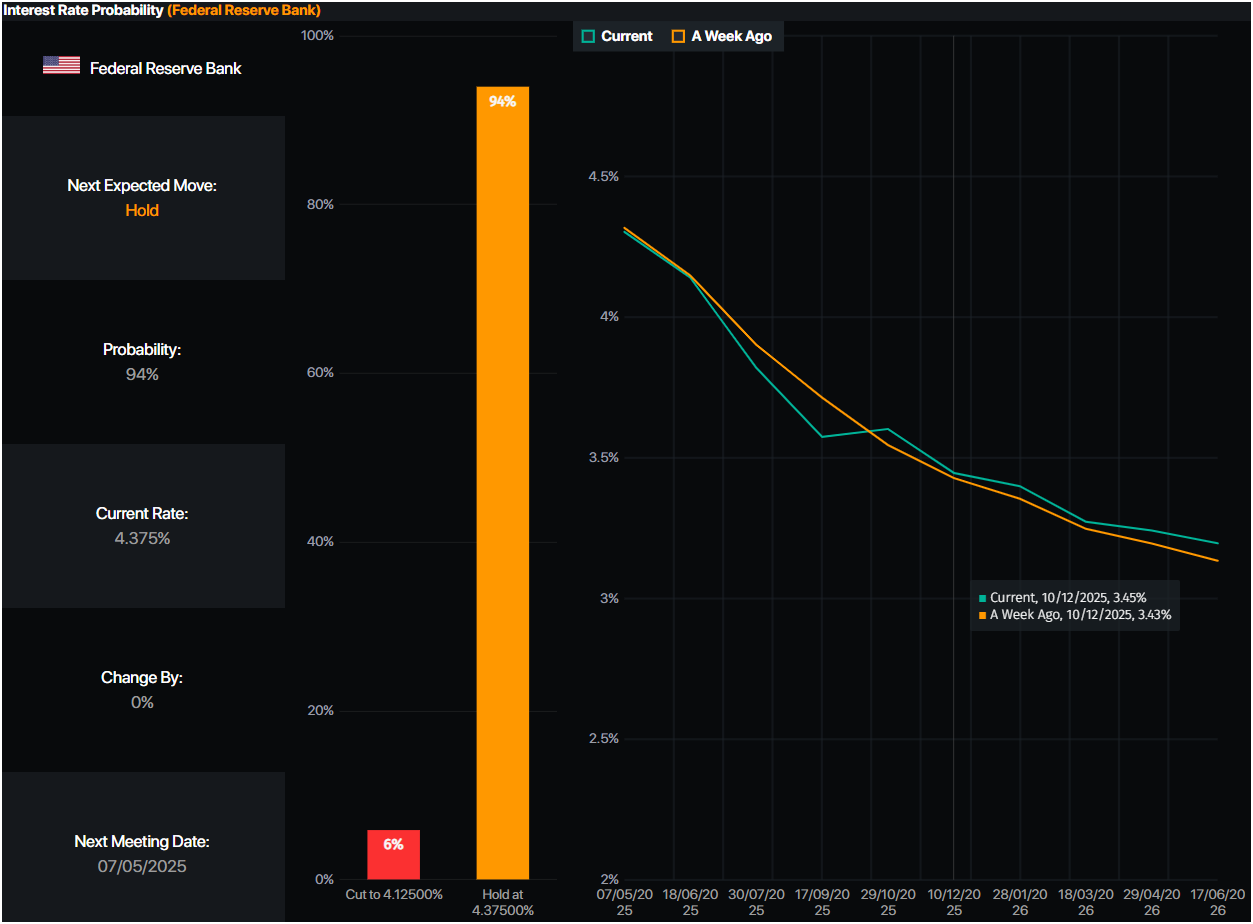
Source: Primer Market Terminal
Daily digest market movers: Gold price tanks below $3,300 on risk-on sentiment
- The US 10-year Treasury yield gains two basis points to 4.371%.
- US real yields are edging up 1.5 bps to 2.099%, as shown by the yields on US 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities.
- Data-wise, S&P Global revealed that the US Manufacturing PMI in April improved from 50.2 to 50.7, contrary to other readings that dipped. The S&P Global Services PMI for the same period dipped from 54.4 to 51.4, below forecasts of 52.8.
- The US economic docket for the week includes Fed speakers, Durable Goods Orders, and the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment final reading.
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price remains bullish despite retreating
Gold remains upward biased despite the ongoing pullback driving the yellow metal below $3,300 a troy ounce. Although it seems that sellers are in charge, they need to drag XAU/USD below the April 3 peak of $3,167, so they could test the next key support level, being the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at $3,032.
Conversely, if buyers reclaim $3,300, the next key resistance would be $3,450, followed by the $3,400 mark.
US-China Trade War FAQs
Generally speaking, a trade war is an economic conflict between two or more countries due to extreme protectionism on one end. It implies the creation of trade barriers, such as tariffs, which result in counter-barriers, escalating import costs, and hence the cost of living.
An economic conflict between the United States (US) and China began early in 2018, when President Donald Trump set trade barriers on China, claiming unfair commercial practices and intellectual property theft from the Asian giant. China took retaliatory action, imposing tariffs on multiple US goods, such as automobiles and soybeans. Tensions escalated until the two countries signed the US-China Phase One trade deal in January 2020. The agreement required structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime and pretended to restore stability and trust between the two nations. However, the Coronavirus pandemic took the focus out of the conflict. Yet, it is worth mentioning that President Joe Biden, who took office after Trump, kept tariffs in place and even added some additional levies.
The return of Donald Trump to the White House as the 47th US President has sparked a fresh wave of tensions between the two countries. During the 2024 election campaign, Trump pledged to impose 60% tariffs on China once he returned to office, which he did on January 20, 2025. With Trump back, the US-China trade war is meant to resume where it was left, with tit-for-tat policies affecting the global economic landscape amid disruptions in global supply chains, resulting in a reduction in spending, particularly investment, and directly feeding into the Consumer Price Index inflation.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.
