Mexican Peso dips as Trump eases rhetoric on Powell and China
- Mexican Peso weakens 0.29% vs USD amid return of Greenback strength and improving market sentiment.
- Trump says he won’t remove Fed Chair Powell, easing investor concerns over central bank independence.
- Mexican Retail Sales disappoint; Citi survey shows trimmed growth, stable Banxico rate cut expectations.
The Mexican Peso (MXN) registered modest losses against the US Dollar (USD) on Wednesday amid an improvement in risk appetite and regained confidence in the Greenback as US President Donald Trump denied that he would remove Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell. At the time of writing, the USD/MXN trades at 19.65, up 0.29%.
The markets remain digesting recent news that US President Donald Trump tempered his attacks on Powell alongside softening its tariff stance on China, aiming to strike a deal with Beijing. The Wall Street Journal revealed that Washington is considering reducing duties on China, though Trump warned that “it wouldn’t be zero.”
Wall Street cheered the breaking news, though later US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent commented that Trump has not offered to lower tariffs on China unilaterally.
In Mexico, Retail Sales in February were lower than expected, according to monthly and annual data from the Instituto Nacional de Estadistica Geografia e Informatica (INEGI). Meanwhile, Citi Mexico revealed its latest expectations survey, in which 34 economists updated their forecasts on economic growth, inflation, the USD/MXN exchange rate and Banco de Mexico (Banxico) monetary policy.
Ahead in Mexico’s economic docket traders brace for the release of Mid-month inflation, and Economic Activity data.
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso loses steam as economists expect Banxico’s cut
- The central bank divergence between Banco de Mexico (Banxico) and the Fed favors further upside in USD/MXN. Banxico’s Governing Council expressed its decision to continue easing the policy. Conversely, the Fed is considered cautious, as some officials have shown concerns about a reacceleration of inflation spurred by tariffs.
- Mexico’s Retail Sales in February dipped from 0.7% to 0.2% MoM, beneath forecasts for a 0.3% increase. In the 12 months to February, sales plunged from 2.7% to -1.1%, showcasing the ongoing economic slowdown.
- Citi Mexico's expectations survey shows that economists expect Banxico to cut its rate by 50 basis points at the May meeting. For the full year, they project the main reference rate to end near 7.75%.
- Regarding the USD/MXN exchange rate, private analysts see the exotic pair finishing at 20.93, up from 20.90. Inflation in 2025 is projected to finish at 3.78%, with core figures at 3.80%, mostly aligned with the previous poll.
- Mexico’s economy is expected to grow 0.2% in 2025, below the 0.3% projected in the prior survey.
- Mexico’s Mid-month inflation in April is expected to rise from 3.67% to 3.79% YoY and core figures to increase from 3.56% to 3.77% YoY.
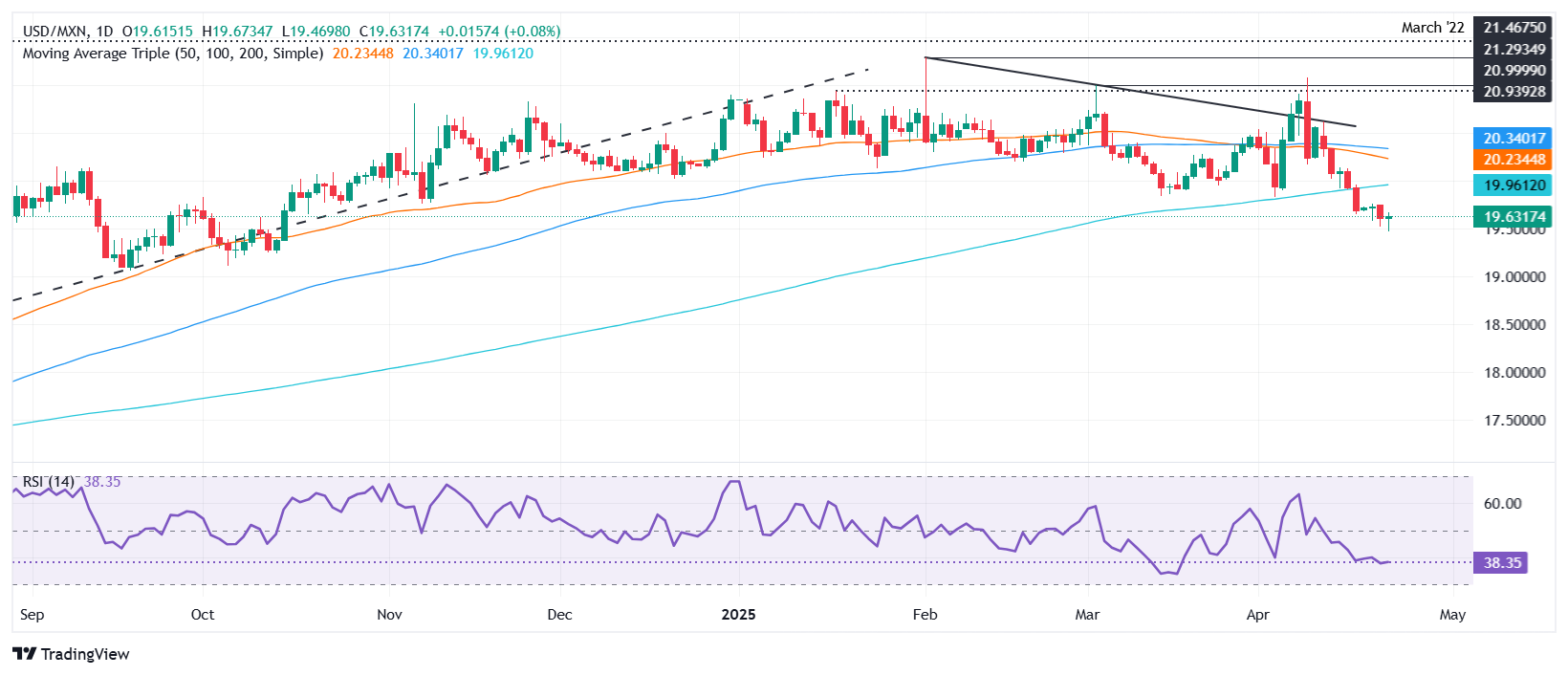
USD/MXN technical outlook: Mexican Peso remains bearish as USD/MXN stays below 200-day SMA
Since dropping below the 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) of 19.91, the USD/MXN has become bearishly biased, though it has recovered some ground after hitting a year-to-date (YTD) low of 19.46.
Buyers must reclaim the 200-day SMA followed by the 20.00 figure for a bullish resumption. A breach of the latter will expose the confluence of the April 14 high and the 50-day SMA near 20.25-20.29 before testing the 100-day SMA at 20.33.
Conversely, sellers could test 19.50 followed by the current YTD low before the 19.00 mark.
Banxico FAQs
The Bank of Mexico, also known as Banxico, is the country’s central bank. Its mission is to preserve the value of Mexico’s currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN), and to set the monetary policy. To this end, its main objective is to maintain low and stable inflation within target levels – at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%.
The main tool of the Banxico to guide monetary policy is by setting interest rates. When inflation is above target, the bank will attempt to tame it by raising rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money and thus cooling the economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN. The rate differential with the USD, or how the Banxico is expected to set interest rates compared with the US Federal Reserve (Fed), is a key factor.
Banxico meets eight times a year, and its monetary policy is greatly influenced by decisions of the US Federal Reserve (Fed). Therefore, the central bank’s decision-making committee usually gathers a week after the Fed. In doing so, Banxico reacts and sometimes anticipates monetary policy measures set by the Federal Reserve. For example, after the Covid-19 pandemic, before the Fed raised rates, Banxico did it first in an attempt to diminish the chances of a substantial depreciation of the Mexican Peso (MXN) and to prevent capital outflows that could destabilize the country.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.
