Gold price languishes near two-week low; seems vulnerable amid hopes for US-China tariff negotiations
- Gold price attracts heavy selling for the third successive day amid a combination of factors.
- Signs of easing US-China tensions and a modest USD uptick weigh on the precious metal.
- Bets for aggressive Fed rate cuts should cap the USD and limit losses for the XAU/USD pair.
Gold price (XAU/USD) retains its bearish bias through the first half of the European session and currently trades around the $3,232 region, just above a two-week low touched earlier this Thursday. The global risk sentiment remains well supported by signs of easing trade tensions between the US and China – the world's two largest economies. Adding to this, some follow-through US Dollar (USD) buying contributes to driving flows away from the safe-haven precious metal for the third straight day.
Meanwhile, a surprise contraction in the US GDP and signs of easing inflationary pressures reaffirmed market bets for a more aggressive policy easing by the Federal Reserve (Fed). This might keep a lid on any further USD appreciation and act as a tailwind for the non-yielding Gold price. Hence, it will be prudent to wait for some follow-through selling before confirming a near-term top for the XAU/USD pair and positioning for an extension of the recent pullback from the $3,500 mark, or the all-time peak.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Gold price bulls remain on the sidelines amid positive risk tone, modest USD strength
- US President Donald Trump said earlier this Thursday there is a “very good probability we'll reach a deal with China” and added that we have "potential" trade deals with India, South Korea and Japan. The comments add to the recent optimism and further boost investors' confidence.
- The US Dollar ticks higher in reaction to Trump's remarks and drags the safe-haven Gold price lower for the third consecutive day on Thursday. A breakdown below the $3,265-$3,260 pivotal support prompts technical selling and further contributes to the intraday decline to a two-week low.
- Automatic Data Processing (ADP) reported on Wednesday that private sector employment rose by 62K in April. This marked a notable decline from the 147K increase (revised from 155K) recorded in March and also missed the market expectation for a reading of 108,000 by a wide margin.
- Adding to this, the advance estimates by the Bureau of Economic Analysis, the US economy contracted at an annualized rate of 0.3% during the first quarter of 2025 after growing at a solid pace of 2.4% in the previous quarter. The data, in turn, revives concerns about a looming US recession.
- Meanwhile, the US Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index eased to the 2.3% YoY rate in March from 2.5% previous. Moreover, the core PCE Price Index, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, rose 2.6% vs. 3% in February, pointing to easing inflationary pressures.
- The dismal US macro data reaffirms bets that the Federal Reserve will resume its rate-cutting cycle in June. Traders are pricing in the possibility that the US central bank will lower borrowing costs by 100 basis points by the year-end. This should cap the USD and support the non-yielding yellow metal.
- On the geopolitical front, Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov said on Wednesday that Russia can mobilize for war on a scale comparable to the Soviet Union during World War II if necessary. Moreover, a Russian drone attack killed two civilians and injured five others in southern Ukraine.
- This might further contribute to limiting losses for the XAU/USD pair. Traders now look forward to key US macro releases – the ISM Manufacturing PMI later this Thursday and the Nonfarm Payrolls report on Friday. The data will provide cues about the Fed's rate-cut path and influence the commodity.
Gold price bears have the upper hand while below the $3,265-3,260 pivotal support breakpoint
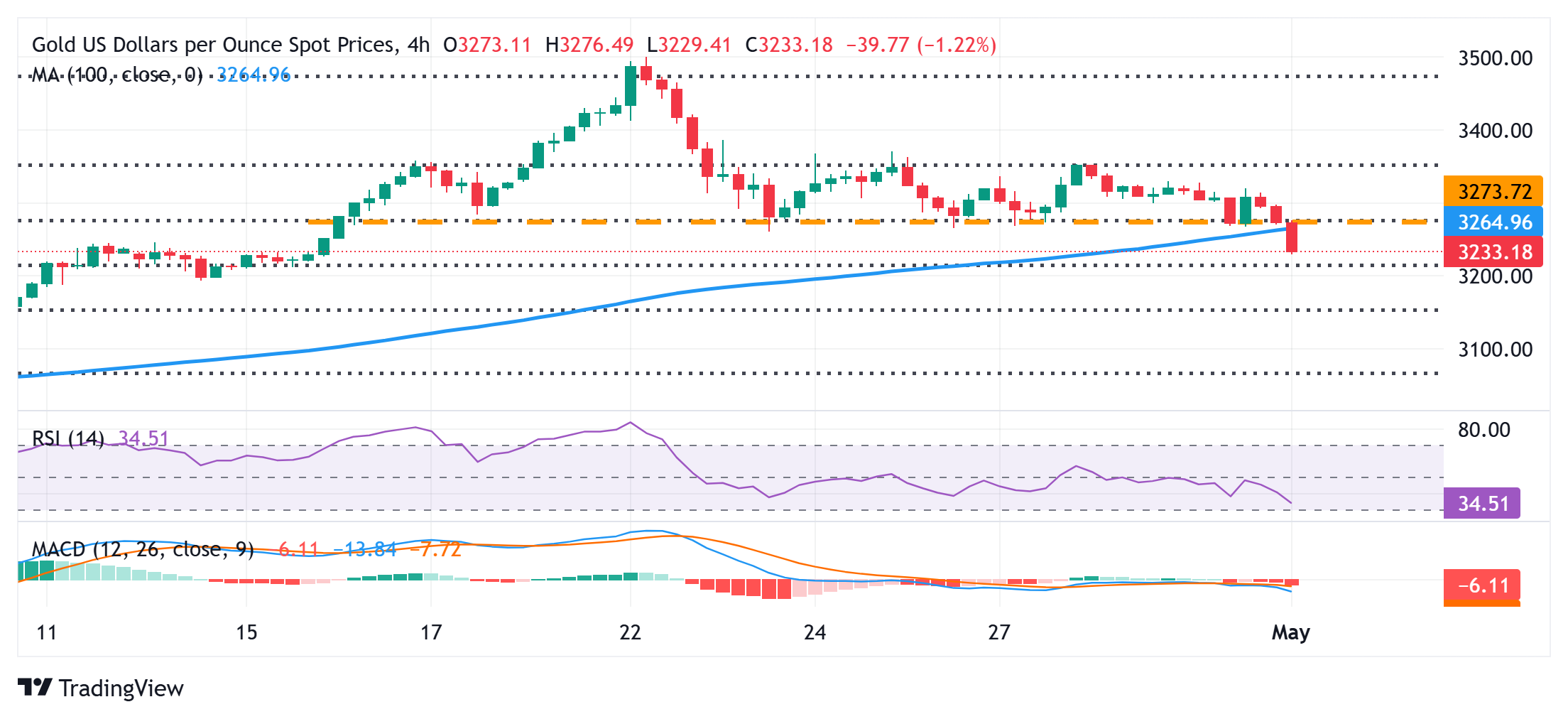
From a technical perspective, the overnight breakdown below the 38.2% Fibonacci retracement level of the latest leg up from the vicinity of mid-$2,900s or the monthly swing low, and the $3,265-$3,260 was seen as a key trigger for bears. That said, oscillators on the daily chart – though they have been losing positive traction – are yet to confirm the negative outlook. Hence, it will be prudent to wait for acceptance below the 50% Fibo. level, around the $3,229-$3,228 region, before positioning for further losses. The Gold price might then accelerate the decline toward the $3,200 round figure en route to the 61.8% Fibo. level, around the $3,160 zone.
On the flip side, any attempted recovery might now confront resistance near the aforementioned support breakpoint, around the $3,260-$3,265 region. This is followed by the 38.2% Fibo. level, just ahead of the $3,300 mark, which if cleared might trigger a short-covering rally and lift the Gold price to the $3,348-$3,350 supply zone. Some follow-through buying, leading to a subsequent strength beyond the $3,367-$3,368 region (23.6% Fibo. level), will suggest that the recent corrective pullback has run its course. The XAU/USD pair might then aim to reclaim the $3,400 mark and extend the momentum further toward the $3,425-3,427 intermediate hurdle before attempting to conquer the $3,500 psychological mark.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.




















